Just as humans need a regular supply of oxygen to survive, businesses require a steady flow of funds to operate and expand. One common and reliable method used today is bill discounting in financial services, which helps businesses unlock working capital tied up in unpaid invoices. Once a business is in running mode, it incurs certain production and distribution expenses. Forced by market considerations and to boost sales and build brand loyalty, most sellers offer their products and services to buyers on credit.
Until the seller receives payment against this product, the funds are blocked. While the payment is awaited, the business has to continue operating. It needs money to pay employees’ salaries, procure raw materials, and other day-to-day expenses. So, there is a requirement for funds to meet such operating expenses.
What is Bill Discounting?
Bill discounting is a smart way for businesses to get early payment for their invoices, helping them manage daily expenses without relying on outside funding sources.
Bill Discounting, also called Invoice Discounting, is a trading activity where a seller sells some goods or services to a buyer. The buyer has to make the payment as per the agreed credit period. Now, if the buyer needs money before that, he can approach a bank or some NBFC and ‘sell’ that invoice to them. The financial institution gets the invoice verified by the buyer and then makes payment to the seller on their behalf. However, they make some deductions, called ‘discount’, as their commission.
So, in a way, the seller gets a discounted payment for their bill. This way, they can run their business operations, and buyers get an extended credit period. On the due date, the seller makes the payment to the financial institution, which completes the cycle for that particular invoice. Since the seller gets payment on a ‘discount’, this transaction is called Bill Discounting.
Example of Bill Discounting:
Here’s a simple bill discounting example (also known as invoice discounting example) Suppose you are in the business of office stationery and have supplied some office stationery to ABC Corporation. The invoice amount is, say, Rs. 1,00,000. Now, AMC Corporation (The buyer) agrees to make the full payment after 30 days.
But if you need the money before 30 days, the buyer will issue you a letter of credit from the bank for 30 days. You can approach the bank and collect payment against that invoice much quicker. For making this ‘advance payment’, the bank will charge some interest to you. So, you will get a discounted amount from the bank. Assuming the discount rate is 5%, the bank will charge you Rs. 5,000 and deposit Rs. 95,000 in your account. At the end of 30 days, the bank will collect Rs. 1,00,000 from the buyer.
This way, that particular invoice would get settled. This financial transaction involving the seller, buyer, and financial institution is called bill discounting or invoice discounting.
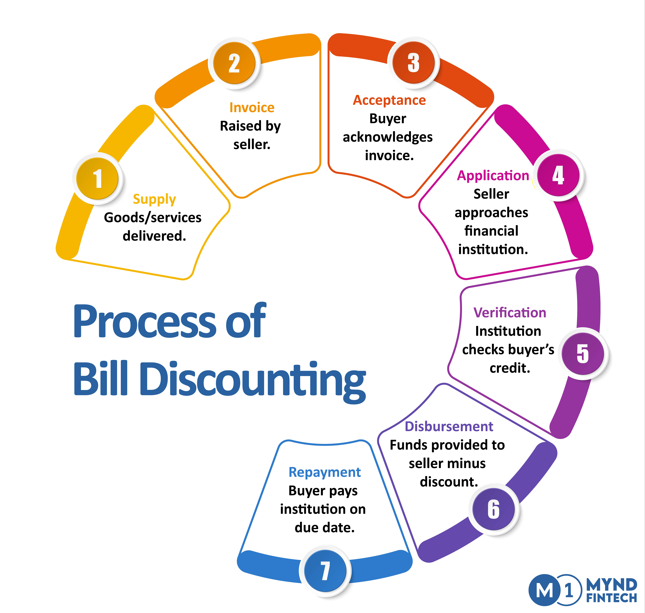
Bill Discounting Process:
- Supply: Goods/services delivered.
- Invoice: Raised by the seller.
- Acceptance: Buyer acknowledges the invoice.
- Application: The Seller approaches a financial institution.
- Verification: The Institution checks the buyer’s credit.
- Disbursement: Funds provided to the seller minus the discount.
- Repayment: Buyer pays the institution on the due date.
For Example
The step-by-step process of bill discounting is given below:
- A seller supplies goods or services to a buyer and raises an invoice.
- The buyer accepts the invoice. This approval means the buyer acknowledges the invoice and promises to make the payment on the due date.
- The seller approaches the financial institution to get the bill discounted.
- The financial institution verifies the creditworthiness of the buyer and the legitimacy of the bill.
- Once approved, the bank disburses the funds to the seller after deducting the pre-defined fee, discount, or appropriate margin.
- Thus, the seller gets a quicker payment for the invoice, which can be used for other business purposes.
- At the end of the original credit period, the buyer makes the payment to the financial institution.
Features of Bill Discounting:
- Evaluating the seller and buyer: Before approving the bill discounting, the bank or NBFC first checks the seller’s reputation and the buyer’s creditworthiness. This is done to ensure that the buyer does not default on making the payment to the bank.
- Making instant cash available for the buyer: It is the most salient feature of bill discounting. The bank or NBFC purchases the invoice and immediately pays after discounting the bill. This makes life easy for the seller. They get an immediate payment and do not need to wait for the buyer to pay the bill.
- Discount Charge: The difference between the face value of the invoice and the amount approved and disbursed by the bank is called the discount. This discount is calculated on the maturity value at a certain percentage per annum.
- Maturity: The maturity date of a bill means the date on which payment of the invoice is due. The average maturity period is 30, 60, 90, or 120 days.
Bill Discounting Rate of Interest:
Most banks and NBFCs do not have a fixed interest rate for discounting bills. Any financial institution considers several factors before deciding on the discount, which may vary from customer to customer.
The various factors that go into consideration for deciding the discounting rate are:
- Financial history and credit score of the seller
- Years of being in the business
- Business volume
- Creditworthiness of the buyer
- Stability of the business and industry
Eligibility Criteria:
The eligibility criteria for bill discounting vary from lender to lender and are generally decided by the management of the respective financial institution offering the service. However, the most common criteria for bill discounting are listed below:
- The company should have been in business for a reasonable period of time. Most financial institutions ask for a minimum of 3 years of being in the business.
- The seller should have dealt with at least 2 investment-grade companies.
- The credit score must be a minimum of 650 or above.
- The business must have a minimum turnover of 1 Crore.
Factors that affect the eligibility:
In addition to the criteria mentioned above, some general guidelines that affect the eligibility for bill discounting are listed below:
- Number of years in the business
- Nature or type of business
- Business Volume and Annual Turnover
- Financial Stability of the seller
- Repayment history and capability of the buyer
- Business Positive Net Worth or Profitability
- Credit rating of a business
- Previous loan defaults, if any
Documents Required for Bill Discounting:
Some of the most common documents required for approving a bill discounting are:
- A duly filled application form with passport-sized photographs
- Business PAN card and address proof
- Applicant’s Aadhar card.
- GST Returns
- Income tax return & Financial statement with an audit report.
- Business Establishment Proof
- Last 12 months’ bank statement
- Bill of Exchange
- Letter of Credit
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing list with all the details
- Logistics details with a copy of the delivery note, if any
- Proof of certificates, registrations, licenses, and permits, if any
- Any other documents required
Benefits of Bill Discounting
Bill discounting, as a financial transaction, is beneficial to all the parties involved – the seller, the buyer, and the financial institution. The buyer and the seller can stabilize their fund flow, while the financial institution can use the funds lying with them and make some profit on it.
The specific benefits of bill discounting are as follows:
- Improves cash flow position: All businesses, big or small, depend on cash flow to survive and grow. Bill discounting facility helps inject a quick cash flow into the business and helps the business survive and flourish. The money received quickly may be used to pay salaries, procure raw materials for the next order, or invest in some new asset.
- Provides instant access to cash: For a seller, a bill discounting facility is a quick and hassle-free way of getting payment against their invoices. It helps them manage their working capital better and keep the working capital cycle short. Most financial institutions like MYND offer funds within 24 to 72 hours.
- No collateral involved: Bill discounting, as a process, is very simple. It does not involve much documentation. Secondly, the seller is not required to provide any collateral security to get the funds. The invoice itself is strong enough collateral to get the funds.
- No debt incurred: Getting funds using a bill discounting facility does not put the buyer under any kind of debt. Here, the buyers get money against the invoices, which are anyway, due to them. It just helps them get the money. So, it does not create any debt liability for them. Compared to traditional financing models, a bill discounting facility is safe from any kind of loss or damage.
- No impact on business sheet: Bill discounting facility does not create any tax liability. It is more of an off-the-book process. So, it has no impact on the balance sheet of the business.
Bill Discounting Versus Business Loan
| S.NO | Comparison Parameter | Business Loan | Bill Discounting |
| 1 | Requirement of Collateral | Collateral Required | Not Required |
| 2 | Processing Time | Long. Usually takes weeks | Quickly within 2-3 days |
| 3 | Suitability | Usually taken for long-term requirements | Suited for short-term requirements |
| 4 | Mode | Generally manually | Completely digital |
| 5 | Document Process | Lengthy & Complex | Simple eligibility criteria |
| 6 | Eligibility Criteria | Very strict | Simple |
| 7 | Impact on the Balance Sheet | Considered a debt, hence impacting the balance sheet | Off the book process. Hence, No Impact on the balance sheet |
Conclusion:
All businesses need money to run their operations. Compared to business loans, bill discounting is a better option to get funds, as the process is quite simple and does not create any kind of liability.
Working with a reputed financial partner like MYND helps the business get the funds at a reasonable discount. With declining interest rates, more and more MSMEs are opting for business discounting as a preferred method of financing their short-term funds’ requirements.
FAQs:
Q1: What is bill discounting meaning?
Ans: Bill discounting meaning refers to a financial process where a seller receives early payment from a bank or NBFC against an unpaid invoice. It helps businesses maintain steady cash flow and meet operating expenses without waiting for the buyer’s payment or relying on external funding. This short-term funding method ensures smooth business operations and is especially useful for MSMEs dealing with delayed payments.
Q2: What is the role of bill discounting in financial services?
Ans: Bill discounting in financial services refers to the process where financial institutions like banks or NBFCs offer early payment to businesses against their unpaid invoices. This helps companies, especially SMEs and MSMEs, to maintain a steady cash flow without waiting for customers to pay. It is a short-term financing solution that ensures smooth operations, timely supplier payments, and better working capital management.
Q3: Is bill discounting a loan?
Ans: Yes, bill discounting is considered a form of short-term financing. The lender advances funds to the seller against unpaid invoices, and the buyer repays the amount on the due date. While it’s not a traditional loan, it functions similarly by offering immediate liquidity against future receivables.
Q4: Can NBFCs offer bill discounting facilities?
Ans: Yes, NBFCs (Non-Banking Financial Companies) are authorized to offer bill discounting services. Many NBFCs provide faster processing, flexible terms, and better digital experiences compared to traditional banks, making them a preferred option for many small and medium businesses.
Q5: What is the repayment period in case of bill discounting?
Ans: The repayment period in bill discounting typically matches the credit period agreed upon between the buyer and the seller—usually ranging from 30 to 120 days. On the due date, the buyer repays the lender directly or through the seller, depending on the arrangement.
Q6. What is export invoice discounting?
Ans: Export invoice discounting is a financing solution that allows exporters to get early payment against unpaid export invoices. Instead of waiting 30–90 days for buyers to pay, exporters receive up to 80–95% of the invoice value upfront from a bank, NBFC, or fintech platform. The financier collects the payment from the buyer later. This helps maintain steady cash flow and manage working capital in international trade.
Q7: How is the interest calculated on discounted bills?
Ans: Interest on discounted bills is calculated using the invoice amount, discount rate, and the credit period—usually 30, 60, or 90 days. The lender deducts this interest upfront before releasing funds. The common formula is: Interest = (Invoice Amount × Discount Rate × Number of Days) ÷ 365. Rates can vary based on the exporter’s credit profile, buyer risk, and lender policies. Some platforms offer dynamic pricing depending on risk assessment and payment history. This ensures exporters receive timely funds while the lender earns a return for the credit period offered.
Q8: Who collects the payment due for the bills discounted?
Ans: The payment for discounted bills can be collected either by the exporter (seller) or the financing institution (bank, NBFC, or fintech platform), depending on the agreement between them. In many cases, the lender directly collects the payment from the overseas buyer on the invoice due date. However, some arrangements allow the exporter to collect the payment and then settle the balance with the lender. The terms are typically defined at the time of discounting.
Q9: Are GST, TDS, and VAT applicable to bill discounting?
Ans: No, GST, TDS, and VAT are generally not applicable on bill discounting. This is because bill discounting is treated as a financial service, not a sale of goods or provision of taxable services. The discounting charge is considered an interest cost, which is exempt from GST under current tax laws. Similarly, since it is not income like fees for professional or contractual services, TDS is also not deducted.
Q10: What is the difference between LC discounting and invoice discounting?
Ans. LC (Letter of Credit) discounting involves a bank guaranteeing payment to the seller, which can then be discounted for early cash. Invoice discounting, on the other hand, is based on outstanding invoices without such a bank guarantee. Both offer liquidity but differ in terms of security and parties involved.
Q11: How does bill discounting help manage working capital?
Ans. A rebate on bills discounted is a financial benefit offered by the lender or bank when the bill is paid off before its due date. Essentially, it is a partial refund of the interest or discount originally charged at the time of discounting. Since the lender recovers the funds earlier than expected, they may return a portion of the unutilized interest to the borrower. This practice encourages early repayment and effectively lowers the cost of borrowing for the business, making bill discounting a more attractive short-term financing option.


